By Sofia Lanchimba Velastegui
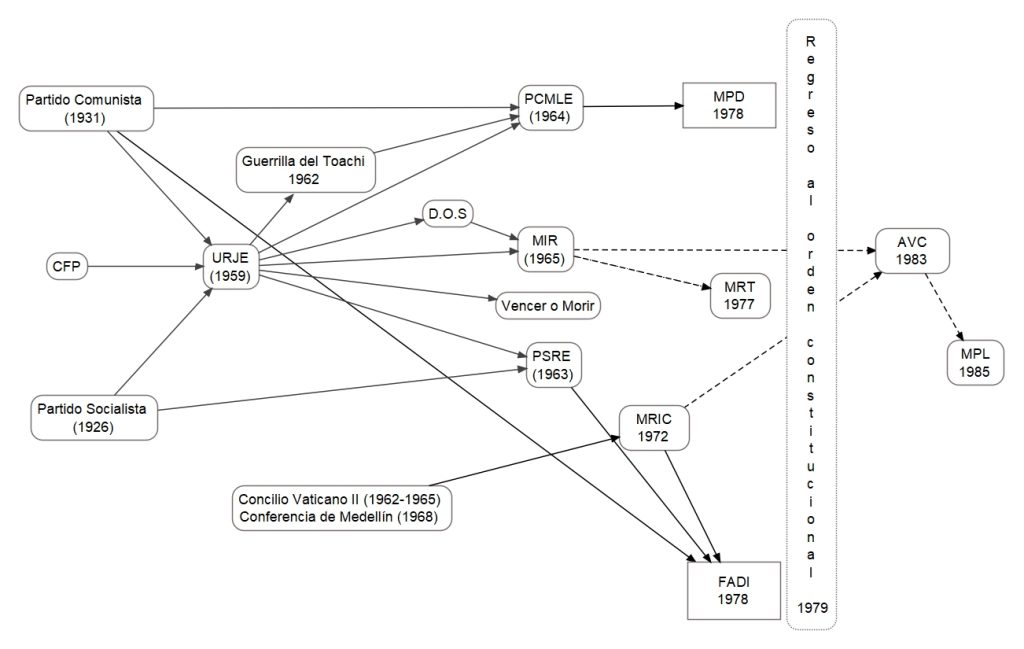
During the 60s and 70s, a process of radicalization took place within the left-wing tradition that would reconfigure the militant camp and political identities. Beginning in 1959 with a massacre in Guayaquil, the increase and radicalization of protests in a scenario of economic crisis and the formation of URJE (Revolutionary Union of Ecuadorian Youth) culminated around 1983, when most of its expressions disappeared, divided, or transformed.
Political activation produced an organizational explosion. Several parties were created located to the left of the Socialist Party (PSE) and the Communist Party (PCE) that had been present in Ecuadorian history since 1926 and 1931 respectively. At the same time, important processes of social mobilization took place. In the 60s the main actor was the student movement and, in the 70s, the trade union movement.
These new parties emerged around debates on revolutionary strategy and realignments regarding Stalinism, the Sino-Soviet conflict, the Cuban revolution, Vatican politics, and anti-colonial revolutions. Thus, there was a multiplication within the left-wing family: communists, socialists, Guevarists, Trotskyists, Maoists, left-wing Christians, etc.
The banana crisis[1] that occurred at the end of the 50s generated a situation of extreme urban and rural poverty with the growth of poverty belts, especially in Guayaquil. The general discontent of the population was evident in Portoviejo in May 1959, and a few days later in Guayaquil. The response of the government, ruled by then-Social Christian President Camilo Ponce Enríquez, was brutal repression. Under the order to “shoot to kill” there was a massacre of between 600 and 800 people[2] which has been silenced in the collective memory.
The massacre of June 2 and 3, 1959 in Guayaquil was the catalyst that ignited revolutionary spirits. One of the flyers drawn up by the Strike Committee the day after the massacre read: “May the blood shed in the streets of Portoviejo and Guayaquil, by our brothers in the cause, be the germ that makes the glorious seed of the Revolution”. Likewise, one of the then-militants claims: “from June 3, 1959, I took an option together with the exploited.” One of the survivors of the massacre, Jaime Galarza Zavala, became one of the most prominent leaders of the radicalized left and one of the notorious targets of the CIA. After the massacre, young militants from the Communist and Socialist Parties, as well as the Concentration of Popular Forces formed URJE.
A generation of militants was radicalized the same year that the Cuban Revolution had taken place. They were not the only ones, the same happened in other parts of the continent. These were years in which the international political markers of the Cold War had a greater weight in the definition of the political field and caused its polarization in a friend-enemy logic. A world divided between the Soviet Union and the United States offered greater possibilities for the strengthening of transnational identities. On the one hand, communism, and the radical left, and on the other, anti-communism and dictatorships were signs of polarization. The different expressions of the left felt more comfortable with their international families than with their countrymen. The Cold War upset the internal balances of force and gave the left the impression of having more weight and strength than they had.
Although URJE was influenced by the Communist Party, it acted with a margin of autonomy. Inside it, a radicalization was brewing against the socialist and communist parties because they demanded the abandonment of the revolutionary project. Linked to URJE, the first attempt to organize a rural guerrilla occurred. In 1962 URJE militants were arrested in the first attempt to reunite what became known as the “Toachi Guerrilla”.
The repression and the failure of the attempts to detonate the guerrilla forced a reorganization of the left and a change of strategy. During the 1970s, the organizations turned towards a mass insurrectionary policy. It was no longer about the guerrilla vanguard. All parties were committed to quantitative growth through the creation of mass fronts. At the same time, the trade union movement gained strength in the 70s, because of incipient industrialization processes. Between 1975 and 1983, the most important national strikes took place.
During the two decades, the left faced dictatorships, counterinsurgent strategies and strong anti-communism whose target was not only the members of the Communist Party or leftist militants, but all expressions of popular discontent. However, the repression only affirmed the revolutionary spirit. The biggest blow came through the legal-political reform of 1979 when Ecuador returned to constitutional order. The entrance to institutional life disarmed the revolutionary organizations. Most of its expressions entered formal political life and those that did not gradually disappeared.
Author’s Bio: Sofia Lanchimba Velastegui is an Ecuadorian sociologist and lawyer. She investigates mobilization and leftist militancy in Ecuador between the 1960’s and 90’s.
References
This article is based on the review of declassified CIA files, flyers and oral interviews with militants collected for the doctoral thesis of the Political and Social Sciences Program, UNAM.
Endnotes
[1] Ecuadorian banana exports fell. The price of essential items increased.
[2] There is no official death toll. The newspaper “El Comercio” recognizes eight dead people, however, testimonies and flyers speak of 500, 700 or 800 dead.
Feature Image: Author’s own.